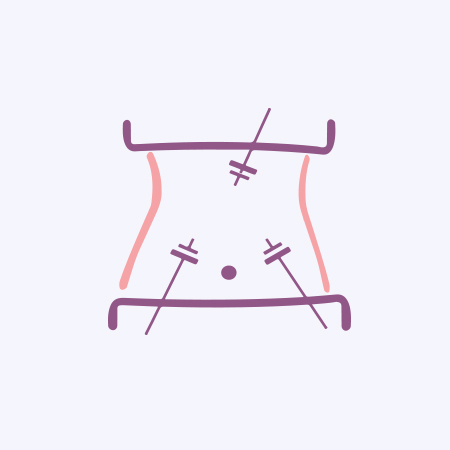
Laparoscopic surgery, often referred to as minimally invasive surgery, is a modern medical technique that has revolutionized the way many surgical procedures are performed. This advanced approach involves making small incisions in the patient's body and using specialized instruments, including a laparoscope (a thin, flexible tube with a camera and light source), to visualize and perform surgery. Here's a detailed description of laparoscopic surgery:
Precision and Minimization: Laparoscopic surgery is designed to minimize trauma to the patient's body. Instead of a large, open incision, the surgeon makes several small incisions, typically less than an inch in size. Through these tiny openings, they insert the laparoscope and surgical instruments. This precision reduces blood loss, post-operative pain, and scarring.
Enhanced Visualization: The laparoscope provides a high-definition, magnified view of the surgical area. This level of visualization allows the surgeon to perform intricate procedures with great accuracy. The surgeon can see the affected area on a screen in real-time, ensuring a precise and safe surgery.
Less Pain and Quicker Recovery: Laparoscopic surgery is known for its quicker recovery times and reduced post-operative pain. Patients often experience shorter hospital stays and a faster return to their daily activities.
Lower Infection Risk: With smaller incisions, the risk of infection is significantly reduced. This benefits the patient and can lead to a quicker return to normal life.
Cosmetic Benefits: The smaller incisions result in minimal scarring, which is a cosmetic advantage for many patients.
Patient Satisfaction: Patients often report higher satisfaction levels with laparoscopic surgery due to the reduced pain and faster recovery.
Hetroscopy
Hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive medical procedure used to examine and treat the inside of the uterus (the womb). It involves the use of a thin, lighted tube called a hysteroscope, which is inserted through the cervix into the uterine cavity. Here's a detailed description of hysteroscopy:
A Glimpse Inside the Uterus: Hysteroscopy provides a direct view of the uterine cavity, allowing healthcare professionals to inspect and diagnose various uterine conditions, such as polyps, fibroids, adhesions, and structural abnormalities.
Minimally Invasive: Unlike traditional open surgery, hysteroscopy is minimally invasive, typically requiring no external incisions. The hysteroscope is inserted through the cervix, eliminating the need for external cuts. This results in less pain, shorter recovery times, and reduced scarring.
Diagnostic and Therapeutic: Hysteroscopy serves both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. During a diagnostic hysteroscopy, the doctor evaluates the uterine lining, identifying any abnormalities. In therapeutic hysteroscopy, if an issue is found, the doctor can often address it during the same procedure, making it a valuable tool for treatment.
Improved Reproductive Health: Hysteroscopy is frequently used to investigate and treat the causes of infertility, recurrent miscarriages, abnormal uterine bleeding, and other gynecological conditions that affect a woman's reproductive health.
Precision and Accuracy: The hysteroscope provides a clear, magnified view of the uterine cavity. This high-definition visualization allows for precise examination and treatment, ensuring that any necessary procedures are performed with accuracy.
Local or General Anesthesia: Depending on the complexity of the procedure, hysteroscopy can be done with local or general anesthesia, ensuring the patient's comfort throughout the process.
High-Risk Pregnancy
A high-risk pregnancy, also known as a complicated or high-risk obstetric pregnancy, is a term used in the field of maternal and fetal health to describe pregnancies that carry an increased risk of complications for the mother, the baby, or both. These pregnancies require special attention and care to ensure the best possible outcomes. Here is a detailed description of high-risk pregnancies:
Understanding High-Risk Pregnancy-
Varied Causes: High-risk pregnancies can result from a multitude of factors, including pre-existing medical conditions (such as diabetes or hypertension), complications that arise during pregnancy (such as preeclampsia or gestational diabetes), advanced maternal age, multiple pregnancies (e.g., twins or triplets), lifestyle choices (such as smoking or substance abuse), and more.
Medical Supervision: A high-risk pregnancy demands closer monitoring and specialized medical care. Healthcare providers, including obstetricians, perinatologists, and neonatologists, collaborate to manage and mitigate potential complications.
Risk Assessment: One of the first steps in managing a high-risk pregnancy is assessing the specific risks and factors that make it high-risk. This often involves a comprehensive medical history review and, in some cases, advanced prenatal testing.
Types of High-Risk Pregnancies:
Medical Conditions: These include pre-existing conditions like diabetes, hypertension, kidney disease, or heart disease, which can complicate pregnancy or require careful management.
Complications of Pregnancy: Conditions like preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, placenta previa, or preterm labor can develop during pregnancy, posing a risk to both mother and baby.
Multiple Pregnancies: Carrying twins, triplets, or more can increase the risk of complications, such as preterm birth or low birth weight.
Advanced Maternal Age: Pregnancies in women over the age of 35 may be considered high-risk due to a higher likelihood of genetic abnormalities and other complications.
Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, substance abuse, or poor nutrition can contribute to high-risk pregnancies.
Management of High-Risk Pregnancies:
Specialized Care: High-risk pregnancies require specialized care. Medical professionals closely monitor the mother's health, perform frequent ultrasounds and tests, and provide interventions as needed.
Individualized Plans: Treatment plans are tailored to the specific needs and risks of each high-risk pregnancy. This may include medication, bed rest, dietary changes, and more.
Communication: Open communication between the healthcare team and the expectant parents is crucial. Expectant parents are encouraged to ask questions, express their concerns, and actively participate in the decision-making process.
Emotional Support: High-risk pregnancies can be emotionally challenging. Emotional support and counseling are often offered to help expectant parents cope with the stress and uncertainty.
Preparation for Birth: High-risk pregnancies may result in the need for a specialized birth plan, such as a cesarean section or induction, depending on the medical circumstances.
High-risk pregnancies require a combination of medical expertise, emotional support, and careful planning. The goal is to ensure the health and well-being of both the mother and the baby throughout the pregnancy, with a focus on reducing potential risks and complications to achieve a successful and safe delivery.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound, also known as a sonogram, is a widely used medical imaging technique that provides real-time images of the inside of the body by using high-frequency sound waves. It is a safe, non-invasive, and versatile tool that helps healthcare professionals in diagnosing and monitoring a wide range of medical conditions.
How Ultrasound Works:
Sound Waves: Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves that are beyond the range of human hearing. A device called a transducer emits these sound waves, which then bounce off internal organs, tissues, and structures in the body.
Echoes: The sound waves create echoes when they encounter different tissues. The transducer receives these echoes and sends the information to a computer, which processes the data in real-time to generate images on a screen.
Real-Time Imaging: The real-time nature of ultrasound allows healthcare providers to observe movement and changes as they occur, making it invaluable for assessing blood flow, fetal development during pregnancy, and more.
Application of Ultrasound:
Pregnancy: One of the most well-known uses of ultrasound is in prenatal care. Obstetric ultrasounds provide images of the developing fetus, enabling healthcare providers to monitor the baby's growth, check for abnormalities.
Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) for Male Partner Cause
IUI is a fertility treatment that involves the injection of sperm inside a woman's uterus to enable fertilisation.
Pregnancy Contraception
Contraception during pregnancy, often referred to as "pregnancy prevention," is a crucial aspect of family planning and reproductive health. While it may seem counterintuitive to think about contraception during pregnancy, it is important for individuals or couples who wish to avoid having additional children in close succession or for medical reasons. Here's a description of pregnancy contraception:
Continuing Control Over Family Planning: Pregnancy contraception is a method used by individuals or couples who wish to exercise continued control over their family planning even when a pregnancy has already occurred. It allows them to make informed choices about the timing and spacing of their children.
Reasons for Pregnancy Contraception:
Spacing: Pregnancy contraception may be chosen to ensure adequate spacing between pregnancies, promoting better maternal and infant health. Health Concerns: In some cases, a pregnancy may pose health risks to the mother or the unborn child. Contraception during pregnancy can help prevent additional pregnancies until health concerns are addressed.
Personal Choice: Some individuals and couples may decide that they are not ready for another child or do not want additional children, and they use contraception to prevent further pregnancies.
Contraception Options: There are several contraception methods that can be employed during pregnancy, including barrier methods (e.g., condoms), hormonal methods (e.g., birth control pills), intrauterine devices (IUDs), and surgical options (e.g., tubal ligation). The choice of method depends on individual circumstances and medical advice.
Medical Guidance: Decisions about contraception during pregnancy should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider. They can provide information about the risks and benefits of each method and help individuals or couples choose the most appropriate option.
Postpartum Considerations: After childbirth, the postpartum period is another important phase for considering contraception. Pregnancy can occur soon after giving birth, and it's essential to plan for contraception during this time as well.
Ensuring Safe and Effective Contraception: Proper use of contraception is vital to ensure its safety and effectiveness. Individuals or couples should follow their healthcare provider's guidance and use the chosen method consistently and correctly.
Contraception during pregnancy is a valuable option for those who want to make informed choices about their family planning journey. It empowers individuals and couples to take control of their reproductive health and make decisions that align with their personal, medical, and family circumstances.